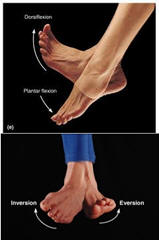
Ankle

Dorsiflexion is backward flexion
(bending), of the foot. This can also be described as bending in the direction
of the dorsum. (dorsum = upper surface = "superior" surface, i.e. the surface of
the foot that includes the toe nails or finger nails).
Plantarflexion
is the opposite movement, the movement of the foot in which the foot flex
downward toward the sole.
Inversion and
eversion refer to movements that tilt
the sole of the foot away from (eversion)
or towards (inversion) the midline of
the body.
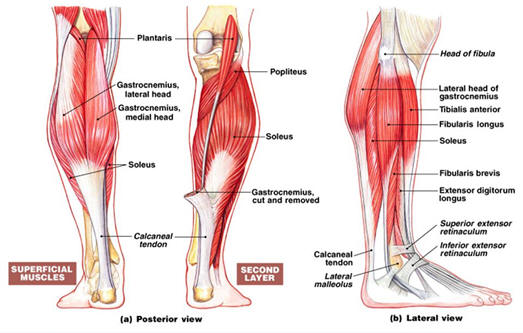
Plantarflexors:
Gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis posterior, fibularis brevis and longus,
flexorhallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus and plantaris. These muscles form
the calf and the posterior compartment of the leg.
Dorsiflexors:
Tibialis anterior, extensor hallicus longus, extensor digitorum longus,
and peroneus teritus.
These muscles are part of the anterior compartment of the
leg (shin).
Eversors:
Peroneus longus, peroneus brevis.
Inversors:
Tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior.
Mobility tests:
Ankle.
Strength tests
: Ankle.
Inline Lunge: ankle inversion or
the lack of stability might cause movement or misalignment of the front knee
during the execution.
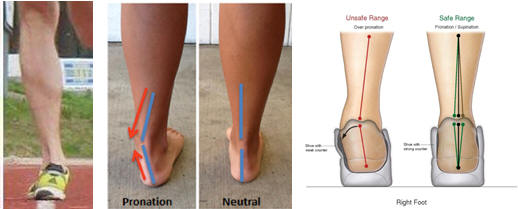 Pronation Too
much eversion causes a de-alignment of the heel relative to the knee-ankle line
known as pronation. This is easily
visible during a posture assessment or during training.
It is likely the result of having long and week eversor muscles and short
and strong inversor muscles. It
will likely influence the alignment of one or more joint above.
Might be caused or made worst if the arc of the foot is weak (flat foot).
Specific evaluation of the mobility of the ankle should be conducted.
Pronation Too
much eversion causes a de-alignment of the heel relative to the knee-ankle line
known as pronation. This is easily
visible during a posture assessment or during training.
It is likely the result of having long and week eversor muscles and short
and strong inversor muscles. It
will likely influence the alignment of one or more joint above.
Might be caused or made worst if the arc of the foot is weak (flat foot).
Specific evaluation of the mobility of the ankle should be conducted.
Strength:
Ankle Eversion
with Elastic Band;
Ankle
Inversion with Elastic Band
Weak ankle
The stability of the
eversion-inversion movements is challenged in several T&F events;

 those
that include running in a curve (ex.: sprints, indoor track running, and high
jump). Those events would require
sufficient mobility and good strength of the eversion-inversion movements.
those
that include running in a curve (ex.: sprints, indoor track running, and high
jump). Those events would require
sufficient mobility and good strength of the eversion-inversion movements.
Strength:
Ankle Eversion
with Elastic Band;
Ankle
Inversion with Elastic Band
While the exact cause is unknown, shin splints can be attributed to the
overloading of the lower leg due to biomechanical irregularities resulting in an
increase in stress exerted on the tibia possibly caused by,
 and variations: Increase ankle strength
and stability.
and variations: Increase ankle strength
and stability.